Digital marketing is continually changing to meet the needs of its users. The arrival of Covid in 2020 turned the digital marketplace on its head, with lockdowns and changing shopping patterns. Allied with this has been the breakdown of many shipping chains and a virtual collapse of just-in-time delivery. These changes have made digital marketing more critical than ever, making clear digital marketing trends evident in this post-Covid world and beyond.


Most Notable Digital Marketing Trends:
1. An Increased Use of Chatbots
With more people doing their research online, combined with a reluctance by many to go in-store, there has been a notable increase in the use of Chatbots over the last couple of years.
Of course, this isn’t just due to increased demand. Chatbots have become more realistic and lifelike in recent years, giving people a much-improved user experience. In addition, advances in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and customer sentiment analysis have all improved the ability of chatbots to interact in a more human-like manner. As a result, firms are enhancing their customer service experience for customers without a sizable increase in investment.
Tidio reported that 88% of customers had at least one conversation with a chatbot during 2021. Their survey found that in addition to customer service and marketing, chatbots are used in other areas such as data collection, human resources, and operations. They are now an attractive option for eCommerce stores, B2B companies, real estate, and even healthcare.
2. Conversational Commerce is Becoming Increasingly Popular
Customer experience (CX) is becoming increasingly more important. Many consumers are willing to pay more for goods and services if they receive a quality experience than merely paying firms selling at the lowest price. Conversational commerce can help improve the customer experience.
Conversational commerce (aka conversational marketing or chat commerce) uses communication platforms and messaging apps, for example, WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger, to market products, communicate with consumers and offer support at each stage of the sales funnel.
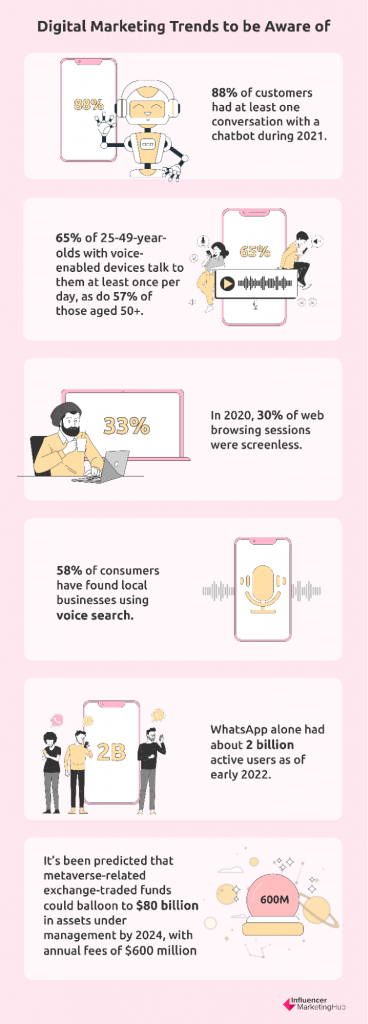

Businesses are discovering how much their customers use messaging apps. Many people consider it a natural evolution to communicate with brands this way, just as they do many of their personal conversations. WhatsApp alone had about 2 billion active users as of early 2022.
3. Voice Search is Becoming Increasingly Popular
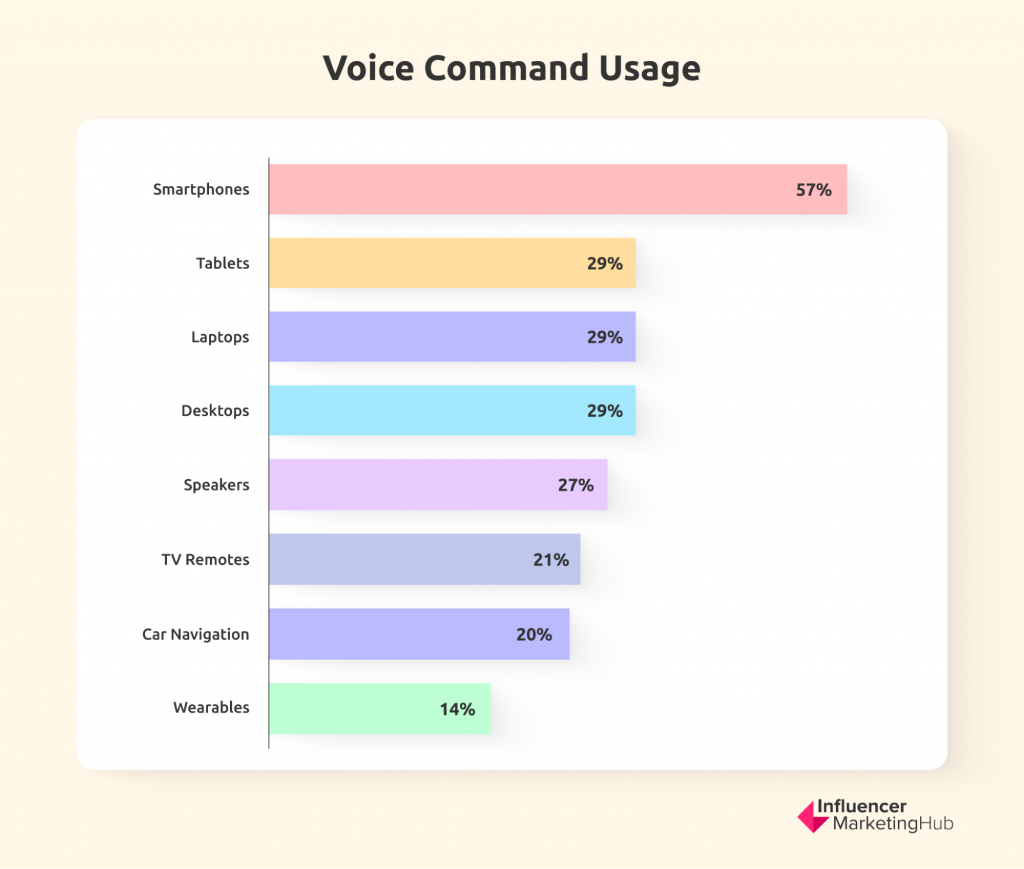
Generation Z, in particular, has never been huge fans of typing. Sure, they have grown up using digital devices, but if they can avoid using a keyboard, they will. Voice search capabilities are increasing to the point that this is now the preferred input method for many. Amazon’s Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri have increasingly become part of everyday life. As far back as 2018, PWC found that people used voice commands on their smartphones (57%), tablets (29%), laptops (29%), desktops (29%), speakers (27%), TV remotes (21%), car navigation (20%), and wearables (14%). And voice search has undoubtedly increased significantly since then.

Surprisingly, it isn’t just the younger generations discovering the ease of voice search. For example, 65% of 25-49-year-olds with voice-enabled devices talk to them at least once per day, as do 57% of those aged 50+.
Gartner discovered that in 2020, 30% of web browsing sessions were screenless. This clearly indicates a shift in how consumers interact with brands online.
Voice search users are increasingly searching for local results. According to Google, searches for “near me” business have increased dramatically over the past few years. Google reports that 58% of consumers have found local businesses using voice search.
Therefore, firms need to adjust their SEO to optimize for voice search. Methods include using natural language with direct answers to specific questions, schema markup and rich snippets, keeping My Business listing and eCommerce store data up-to-date, and ensuring all content is optimized and current.
4. A Movement Towards Omnichannel Digital Marketing
Brands are discovering the benefits of creating campaigns that cover a range of digital marketing channels. This helps them reach a wider audience. In addition, most people don’t restrict themselves to a single digital channel, and omnichannel marketing allows brands to utilize the strengths of multiple channels.
The key to omnichannel marketing is to use all your channels to create a unified experience for each customer. Indeed, true omnichannel marketing doesn’t restrict itself to digital marketing. Instead, it includes some traditional marketing channels in its mix, recognizing that people aren’t 100% digital yet. Each channel interacts to create a unified voice and message for the brand.
Omnichannel marketing recognizes that consumers use a variety of channels at different stages of their day. For example, they may begin their day looking at Facebook before shifting to Instagram. Then they may check their emails. By this point, it’s time to go to work, with the radio playing as they go. On the way home, they may stop at the supermarket, see point-of-sale advertising, and listen to Spotify on their travels. Finally, they may stream a TV program or surf the net on their phone or tablet in the evening. This gives many potential touchpoints for a brand to reach consumers, delivering a unified but not identical message.
Note that omnichannel marketing subtly varies from multichannel marketing. Omnichannel marketing requires a transparent integration of your marketing efforts between your channels. For example, you’re not going to use identical PPC ads on all your social platforms, boring consumers with repetition. Yet nor are your messages so different that they may as well be separate campaigns. All marketing by a brand to a customer coordinates and tells part of a larger story in a seamless, unified way.
5. The Metaverse is Beginning to Have a Large Impact on Digital Marketing
In 2021 Facebook (the company) rebranded to Meta. Considering the size and influence of Facebook’s assets that weren’t Facebook (the platform), separating the naming of the platform and the company made sense. At the time of the rebranding, Mark Zuckerberg announced that the company would be placing its future on its metaverse.
Bloomberg predicts that metaverse-related exchange-traded funds could balloon to $80 billion in assets under management by 2024, with annual fees of $600 million.
The metaverse includes live entertainment, social networks, hardware, user-generated content, and technology infrastructure. It’s a shared virtual space where megatrends converge. It incorporates a multitude of virtual and augmented experiences. In the metaverse, users create avatars and move through a 3D world, interacting with others and the environment around them. The metaverse includes platforms such as Roblox, Minecraft, and Fortnite.
As people spend more time in the metaverse, the line between the real and virtual world is increasingly blurred. As a result, people are beginning to experience brands and even buy virtual products. For example, Vans collaborated with Roblox to create a virtual skate park. Here, they could practice their virtual skateboarding skills and then buy Vans products without leaving the metaverse.
6. SEO is Adapting
Google rolled out a significant Page Experience update in 2021. This update integrated a new set of metrics known as Core Web Vitals into what Google traditionally referred to as “page experience.” Core Web Vitals are the baseline requirements for a site’s technical health. They effectively measure the user experience (UX) of a webpage, covering three main areas: loading, interactivity, and visual stability. These metrics measure how long it takes a user to get to your page, how easily the user initially interacts with it, and whether the user becomes disoriented due to inconsistencies in your page design.
The Page Experience update combined core web vitals with more traditional factors such as being mobile-friendly, safe browsing, HTTPS (as compared to merely HTTP), and having no intrusive interstitials.
Google has also highlighted the importance of the “People also ask” part of its search results. Indeed, it now shows up in about 48.6% of searches, often prominently placed above position one in a search. Therefore, as a marketer, you should include answers to common questions in your content.
You might notice that quite a few of the more established pages on the Influencer Marketing Hub include FAQs. And Google is smart enough to select appropriate answers, even if the wording of what people ask is different from the exact wording on the page. So, for example, at the time of writing, if you search for “influencer marketing,” our Ultimate Guide tops the list.
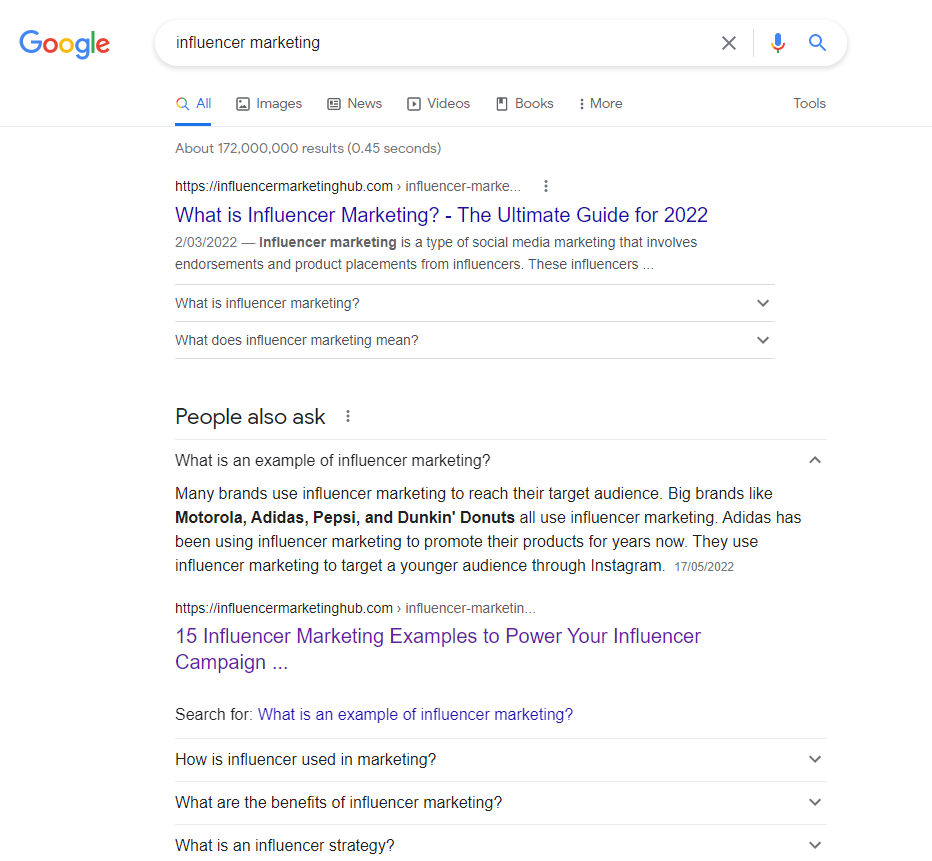

However, you will notice that Google has also included a “People Also Ask section,” and the first question is “What is an example of influencer marketing?” Google has selected a section from the FAQ in our 15 Influencer Marketing Examples to Power Your Influencer Campaign Planning post as the best answer for this question. However, when you look closely at the post, you can see that the actual question in the FAQ is “What brands use influencer marketing?” Despite being worded differently, Google’s algorithm is clever enough to recognize the similarity between the two questions.


In 2022, Google is all about user intent, rather than relying too closely on the words they use in their search.
7. Email Marketing Isn’t Going Anywhere
With email marketing being one of the oldest forms of digital marketing, it is perhaps inevitable that people have been predicting its demise for some years. Yet email marketing isn’t going anywhere in a hurry.
According to The Radicati Group, the total number of business and consumer emails sent and received per day exceeded 293 billion in 2019 and is forecast to grow to over 347 billion by year-end 2023. Worldwide email users are expected to reach 4.3 billion by that time. In addition, Litmus reports that email drives an ROI of $36 for every dollar spent, higher than any other channel.
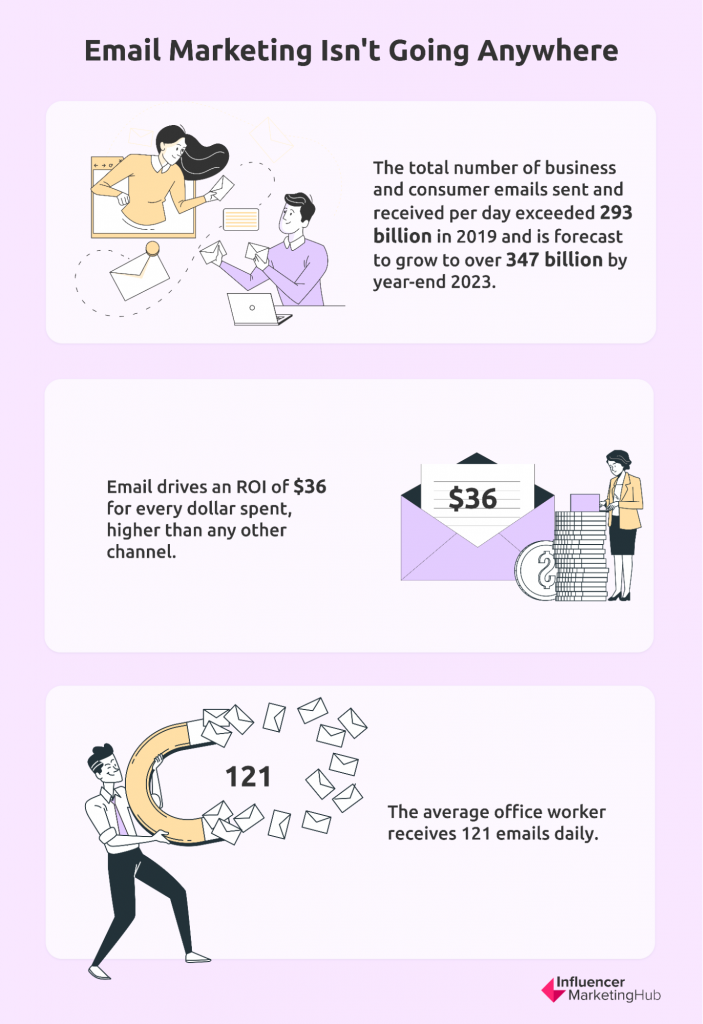

However, personalization is now vital for successful email marketing. People have to opt-in for email marketing and are very conscious about their privacy. Therefore, they don’t take kindly to generic, irrelevant emails. They receive many emails each day – indeed, DMR reports show that the average office worker receives 121 emails daily – so it takes something special to entice somebody to open your emails. Personalizing your marketing emails helps you to improve their effectiveness. Some businesses are now using AI to create custom and tailored emails for specific clients.
8. TikTok is Not Just for Kids
We have been covering the rise of TikTok since the days when Musical.ly still existed as a stand-alone platform. However, it has sometimes been difficult to convince brands that it is a serious social media platform. We regularly update our TikTok Statistics article and have noticed how rapidly TikTok has grown in popularity.
If you still doubt TikTok’s worthiness for serious digital marketing, consider some of these figures:
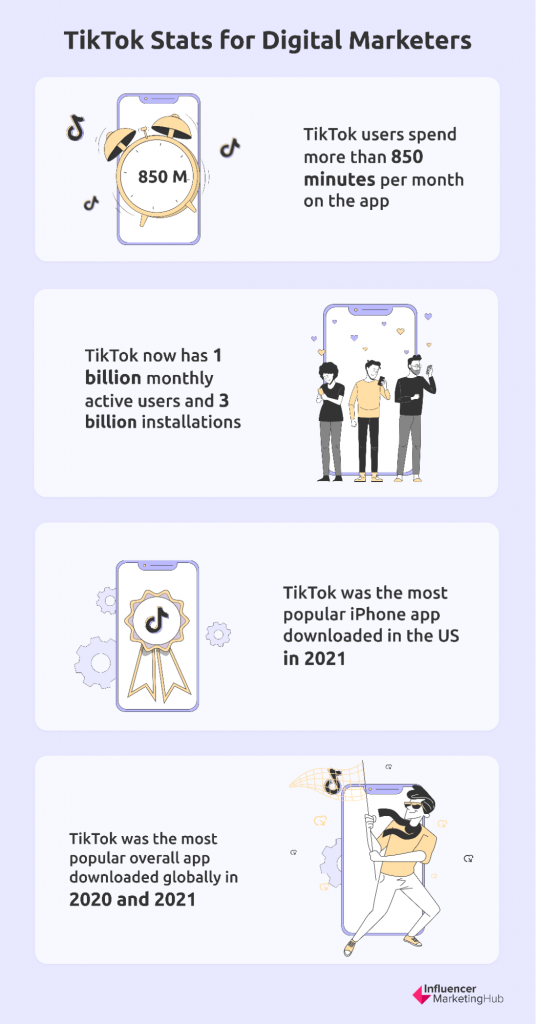

- TikTok users spend more than 850 minutes per month on the app
- TikTok now has 1 billion monthly active users and 3 billion installations
- It was the most popular iPhone app downloaded in the US in 2021, ahead of YouTube, Instagram, Snapchat, and Facebook.
- Indeed, TikTok was the most popular overall app downloaded globally in 2020 and 2021
Like Facebook (and Instagram), TikTok now has a formal advertising marketplace, making it easy for brands to advertise on the platform.
And yes, TikTok is still most popular with the younger generations, with 32.5% of its US users aged 10-19, but its audience is gradually aging. TikTok users don’t appear to be “growing out” of the platform any more than Facebook users have grown out of that app.
9. Amazon’s Reign as the King of eCommerce Continues Unchallenged
Amazon continues to reign supreme as eCommerce’s leader. Although visitors to Amazon.com fell to 2.2 billion in February 2022, this really just reflected fewer Covid-related lockdowns around the world, increasing shoppers’ choices.
However, Amazon is not loyal to any brand other than its own. Virtually anybody can sell on Amazon, giving many opportunities for brands wishing to market online. Amazon Advertising continues to grow and is essential to the company’s revenue. Amazon’s ad revenue was more than $31 billion in 2021, three times its 2018 ad revenue. Amazon continues to refine its ads platform to give more options and data to improve your Advertising Cost of Sales (ACoS).
If you’re not yet selling on Amazon, we have a Complete Guide to Amazon Advertising to help you get started on the platform and an A to Z Guide to Selling on Amazon.